3: labupdate
import java.sql.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class labupdate {
static {
try {
Class.forName("COM.ibm.db2.jdbc.app.DB2Driver");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("\n Error loading DB2 Driver...\n");
System.out.println(e);
System.exit(1);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
String deptno = "";
int updateCount = 0;
String sqlstmt = "UPDATE JLU.STAFF SET SALARY = SALARY * 1.05 WHERE DEPT = ?";
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Connect statement follows:");
Connection sample = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:db2:sample", "db2admin", "db2admin");
System.out.println("Connect completed");
/****************** Turn autocommit to off **************************/
/* ( 4 ) Turn autocommit to off */
/*********************************************************************/
sample.setAutoCommit(false);
/* Print instruction lines */
System.out.println("This program will update the salaries for a department");
System.out.println("\n");
System.out.println("Please enter a department number: \n");
/* Get the department number from the input data */
deptno = in.readLine().trim();
/* Issue Select statement */
System.out.println("Statement stmt follows");
try {
/****************** Create the PreparedStatement object ************/
/* ( 5 ) Create the PreparedStatement object named pstmt using the */
/* prepareStatement method */
/*******************************************************************/
PreparedStatement pstmt = sample.prepareStatement(sqlstmt);
/****************** Set the parameter marker **********************/
/* (6) Set the parameter marker to be value of the department. */
/* This value is placed in the field deptno */
/*******************************************************************/
pstmt.setString(1, deptno);
/****************** Execute the SQL statement *********************/
/* (7) Execute the SQL statement */
/* The number of rows modified by the update statement should */
/* be saved in the variable named updateCount */
/*******************************************************************/
updateCount = pstmt.executeUpdate();
sample.commit();
System.out.println("\nNumber of rows updated: " + updateCount);
} // end try
catch (SQLException x) {
/****************** Handle SQL Exception **************************/
/* (8) An error has occurred. Retrieve the SQLCode */
/*******************************************************************/
int SQLCode = x.getErrorCode();
String SQLState = x.getSQLState();
String Message = x.getMessage();
System.out.println("\nSQLCODE: " + SQLCode);
System.out.println("\nSQLSTATE: " + SQLState);
System.out.println("\nSQLERRM: " + Message);
}
System.exit(0);
} // end main
} // end of labupdate class
这里前面的取消自动提交语句就起作用了,防止了更新失败后的数据丢失。
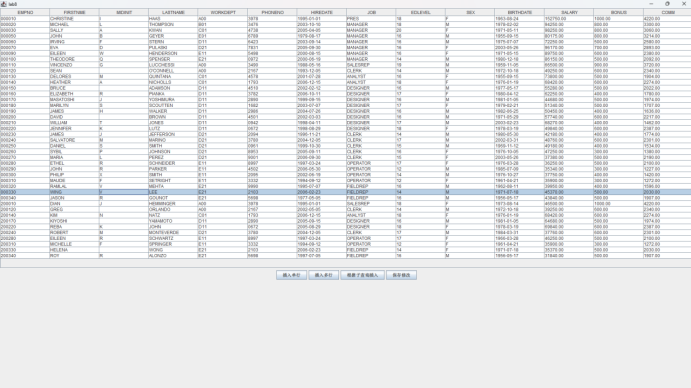
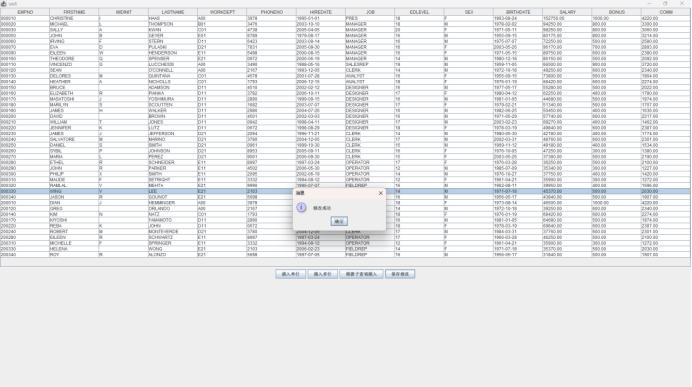
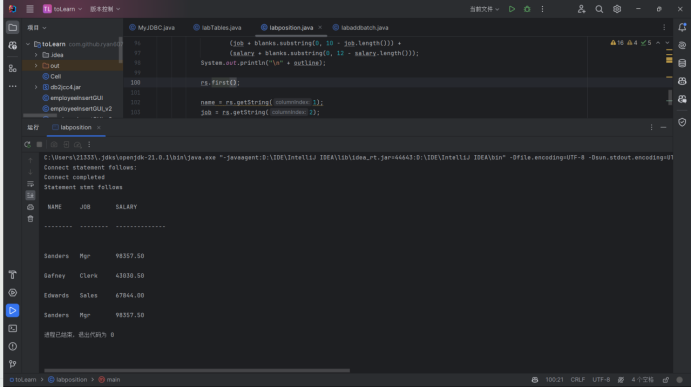
运行结果:
需要注意的几个点:
-
由于是更新操作,所以需要使用
executeUpdate()方法,而不是executeQuery()方法。//创建PreparedStatement对象 PreparedStatement pstmt = sample.prepareStatement(sqlstmt); //设置参数 pstmt.setString(1, deptno); //整型变量updateCount用于保存更新的行数 updateCount = pstmt.executeUpdate(); -
这里出现了手动提交的操作,在完成所有的更新操作后,需要使用
commit()方法进行提交。sample.commit(); -
错误处理,这一点在实验二就有出现,但是在实验3才算正式使用
catch (SQLException x) { int SQLCode = x.getErrorCode(); String SQLState = x.getSQLState(); String Message = x.getMessage(); System.out.println("\nSQLCODE: " + SQLCode); System.out.println("\nSQLSTATE: " + SQLState); System.out.println("\nSQLERRM: " + Message); } -
用设置参数的方式,代码更加灵活,方便用户与程序进行交互。
pstmt.setString(1, deptno);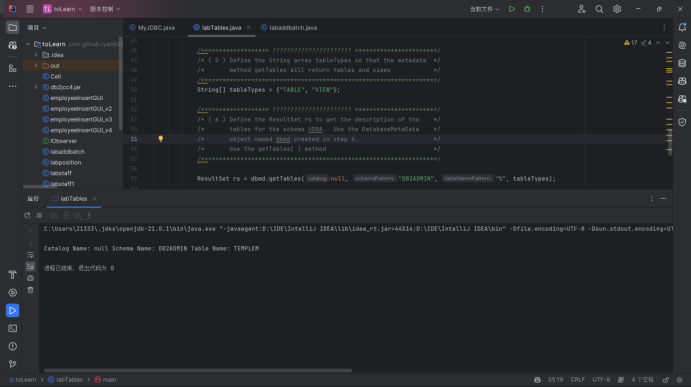
-
关于正常执行,返回0行和溢出:“salary”列被定义为“DECIMAL(10,2)”,这意味着它最多可以存储10位数字,其中包括小数点的后两位,如果薪水增加后的值超过了这个范围,就会发生溢出错误。如果返回0行,则是没有手动提交更新内容,导致操作无效,返回更新行数变成0行。